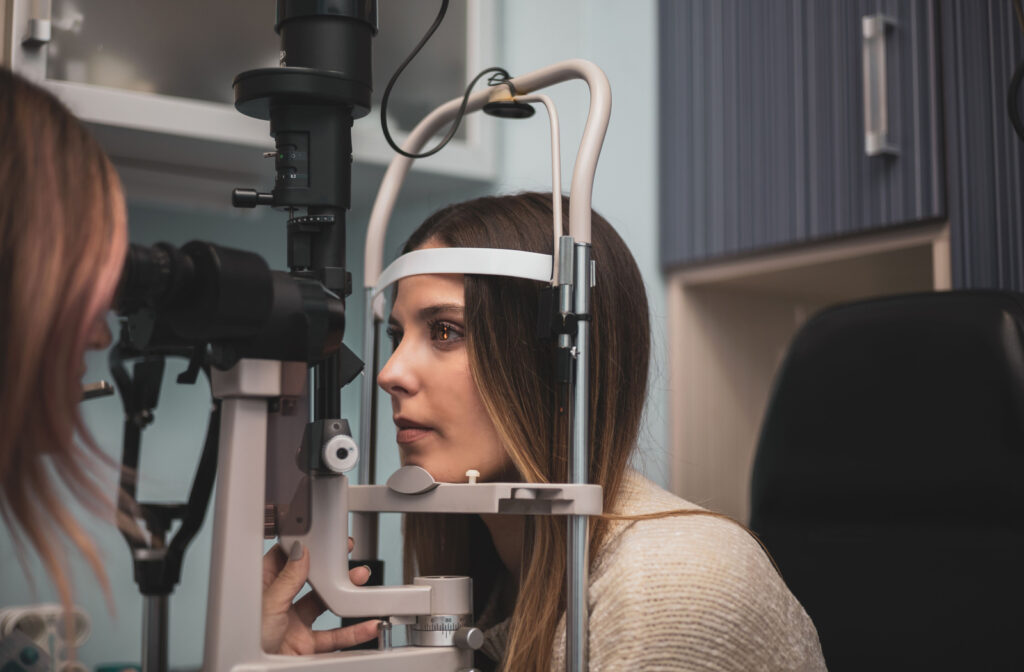
A routine eye exam can reveal more about your overall health than you might expect. During an eye exam, your eye doctor will complete a full evaluation of your vision and ocular health, which can give some valuable insights into your overall health.
Some of the testing done during a comprehensive eye exam can detect signs of medical conditions beyond your eyes, including diabetes.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition that affects millions of Americans. The condition is characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin.
Two of the most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. The risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as well established as type 2 diabetes. However, you may be at a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes if you have a family history of the condition.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, can often be attributed to demographic and lifestyle factors, such as:
- Body weight
- Age
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- History of gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy)
- Genetic background
Early detection of either type of diabetes is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. While most people are familiar with blood tests for diagnosing diabetes, you may be surprised to learn that the condition can also be detected through a routine visit with your eye doctor.
The Link Between Diabetes & Your Vision
Several eye conditions are associated with diabetes, making routine eye exams an important tool for diagnosing and managing the condition.
Diabetic Retinopathy
High blood sugar levels caused by diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to a condition called diabetic retinopathy. In many cases, diabetic retinopathy can develop without any noticeable symptoms in its earliest, most treatable stages. This makes an eye exam all the more crucial for individuals with diabetes who are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Once the condition reaches a certain stage, it can begin to affect your vision. Common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Seeing floaters
- Blurred vision
- A dark or empty spot in the center of your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
Diabetes & Other Eye Conditions

In addition to diabetic retinopathy, having diabetes can also put you at an increased risk of developing other eye conditions, such as macular edema, glaucoma, and cataracts.
- Macular edema: Diabetic macular edema can develop as a complication of diabetic retinopathy. The condition affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. It occurs when fluid accumulates in the macula, causing it to swell and impair vision.
- Glaucoma: Diabetes can increase your risk of developing glaucoma, a group of eye conditions that can damage your optic nerve and lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
- Cataracts: High blood sugar levels caused by diabetes can also affect the lens of your eye, causing cataracts to form. Cataracts lead to clouding of the lens, resulting in blurry vision and vision loss.
Detecting Diabetes with an Eye Exam
A routine eye exam involves much more than just a vision test. During an eye exam, your eye doctor will conduct a full examination of your vision and ocular health, including a variety of tests that can help examine the structure of your eye and spot conditions like diabetes.
Retinal Imaging
Your eye exam may include an assessment of your retina, which can help detect early signs of diabetes. Your retina plays a crucial role in how you process images, and uncontrolled blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels of the retina.
Your eye doctor may take an image of your retina using advanced diagnostic technology, or you may require a dilated eye exam. Both of these tests can allow your eye doctor to gain a clear view of your retina, which can help them identify any signs of retinal damage, such as the presence of small hemorrhages or swelling blood vessels. These abnormalities are early indicators of diabetes and can help inform your healthcare team of what may be needed for further diagnosis and treatment steps.
Ocular Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Another common test for screening and monitoring diabetes is an OCT scan. This scan can produce detailed images of the layers of your retina, which can play a key role in the early diagnosis of diabetes.
Additional Screening
It is important to note that the presence of retinopathy does not necessarily mean that a person has diabetes. Other factors, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels, can also cause retinal damage. Therefore, an eye exam alone cannot definitively diagnose diabetes, but it can serve as an important indicator that further testing is needed.
Your Partner in Eye Care
Routine eye exams are an essential part of both screening for diabetes and monitoring your overall eye health. By working in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and overall diabetes management, eye exams contribute to a comprehensive approach to diabetes care.
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, individuals with diabetes can maintain clear and healthy vision. Our team at Danville Optometric Group is here to support all of your vision care needs, including the need for diabetic eye exams and personalized treatment plans.Schedule an appointment with us today to get support for your vision and long-term eye health.